|
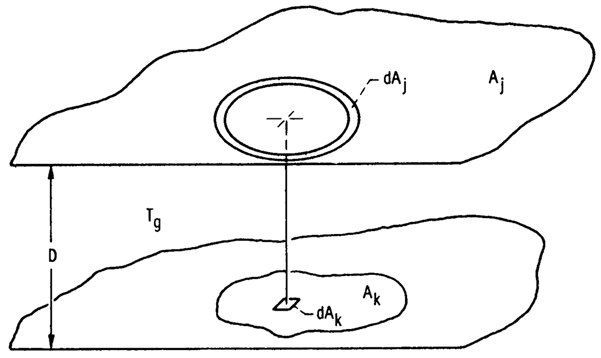
A.5 Infinite Plate to Any Area on Parallel Plate
In Fig. A-5 consider on one plate an element dAk,
and on the other plate a concentric ring element dAj centered
about the normal to dAk. The geometry is like that in Fig. A-2
for a ring on the top of a cylinder to the center of its base. Then, from (A-6),
where kλD
is the optical spacing between the plates. By using the procedure leading to
(A-8), the integral is transformed to
FIGURE A-5 Isothermal layer
of medium between infinite parallel plates. |